Workplace tips from your team at Clarington Physiotherapy Health and Wellness Centre:
Did you know your brain can be under-stimulated during a typical workday? This is especially true for those who have a seated computer job.
Fun fact: sitting for prolonged times staring at a computer can under-stimulate and over stimulate different parts of the brain.
This isn’t ideal as human beings are meant to be active creatures on high alert. But since these computer jobs have entered the picture, the human brain is being rewired and problems are resulting from it.
When sitting at a computer, we over stimulate the parts of our brain that are responsible for vision intake, near vision, and our sympathetic nervous system (the nervous system responsible for dealing with high levels of stress).
Additionally, sitting at a computer UNDER stimulates the parts of our brain responsible for movement, sensation, coordination, balance, upright extension (sitting up straight), peripheral vision, eye muscle strength, posture system, and our parasympathetic nervous system (the nervous system responsible for relaxing).
Obviously, quitting that computer job is not the answer. That said, try these postural ergonomic exercises to help support better brain function, posture, and improve productivity.
1) MOVE. Implement more movement at work
- Every hour, stand up, and move. Go to the washroom, move your wrists and ankles incircles, walk and talk, etc.
2) Posture breaks, controlled breathing, and mindfulness
- Extend neck, extend arms, drop shoulders, close eyes, focus on controlled belly breathing, and be mindful of the top of your head down to your toes, and back up to your head.
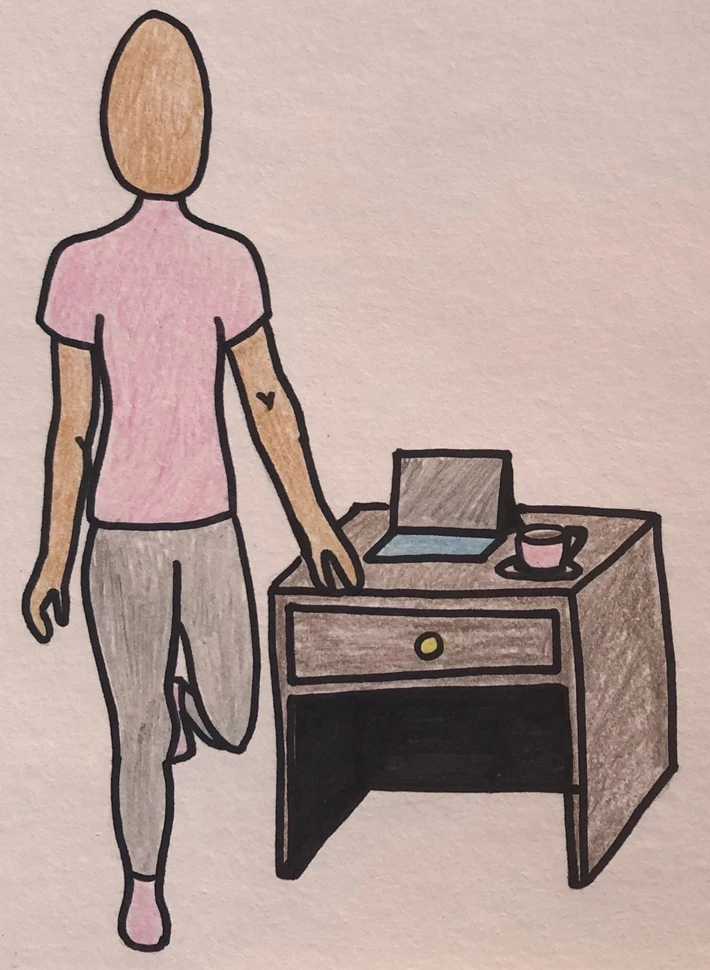
3) Balance and coordination
- Balance on one leg
- Active sitting i.e Try sitting on an exercise ball or posture cushion – creating an unstable surface will force your body to balance itself when sitting.

4) Avoiding computer vision syndrome (i.e. forward head posture, bombarded by blue light and artificial light)
- Near and far exercises (i. 20/20/20 vision break: every 20 minutes, for 20 sec, look 20 yards away.)
- Peripheral vision (Do large eye circles or H)
- Reduce distracting notifications (Reduce audio and visual notifications on your phone and corner of computer screen as it creates loss of focus.)
If you have any questions, or think that your workplace could be contributing to your pain, come in for an assessment today!